The Mighty DCS World F-4 Phantom: A Comprehensive Guide.
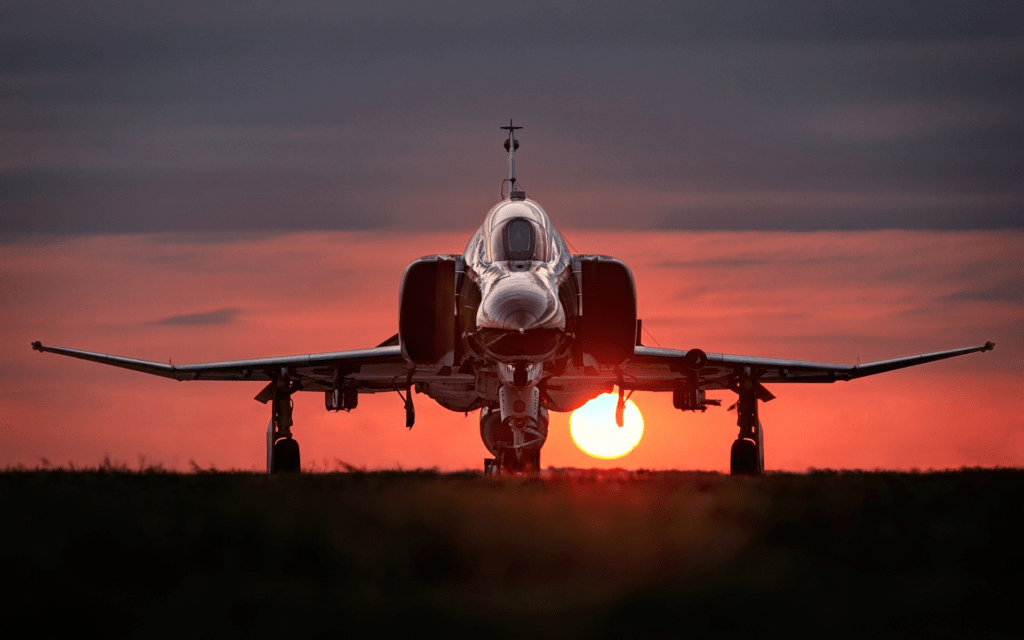
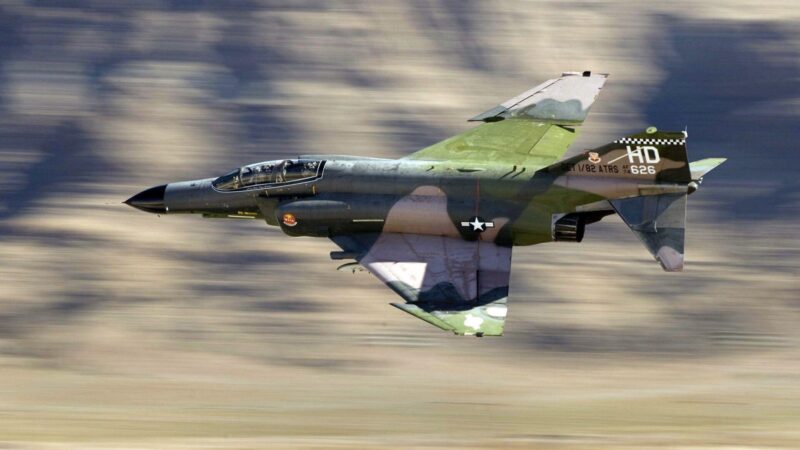
The McDonnell Douglas F-4 Phantom II is one of the most iconic military aircraft ever built, celebrated for its versatility, power, and success across decades of combat. In DCS World, the F-4 Phantom module brings this legendary aircraft to life with an unparalleled level of detail and accuracy.
This post delves into the F-4’s history, features, performance, and combat legacy while comparing its real-world capabilities to its representation in DCS World.
A Brief History of the F-4 Phantom
The F-4 Phantom first flew in 1958, developed as a supersonic, long-range, all-weather fighter-bomber for the U.S. Navy. Its groundbreaking twin-engine design and multi-role capabilities quickly made it a staple of the U.S. Air Force, Navy, and Marine Corps, as well as the air forces of 11 allied nations.
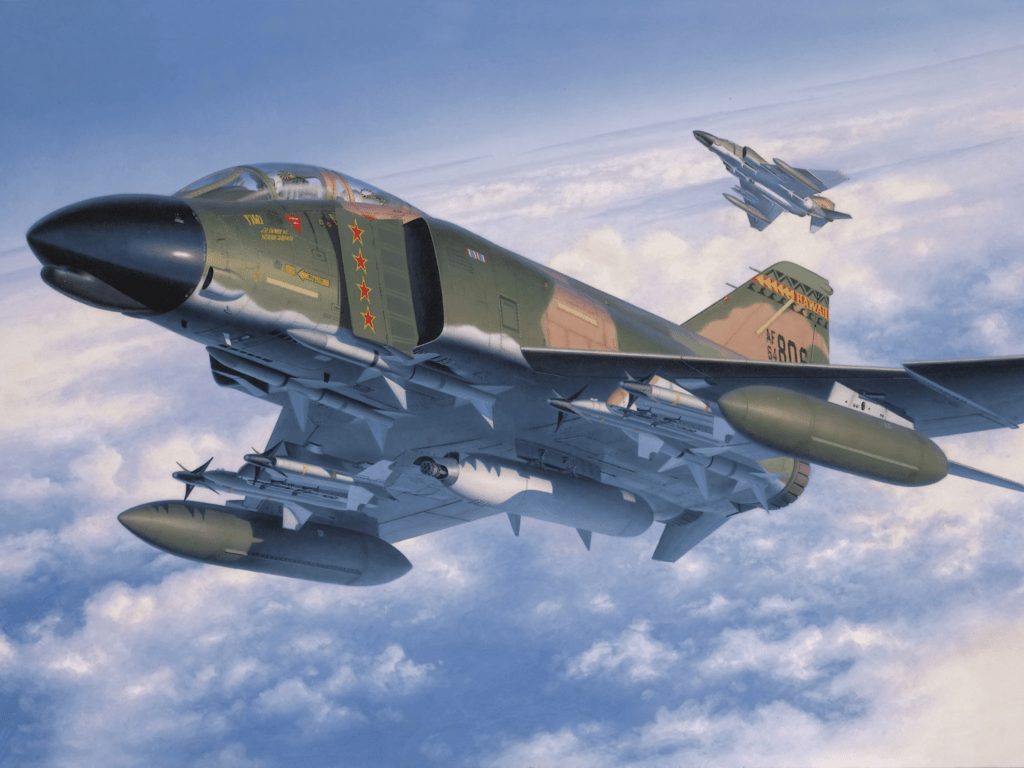
Key milestones in its development include:
- 1960s: Adoption by the U.S. Air Force and Navy for air superiority, reconnaissance, and ground-attack missions.
- Vietnam War: The Phantom became a workhorse, engaging in dogfights, bombing runs, and reconnaissance.
- Cold War: Its versatility ensured its use in NATO and allied forces during key conflicts, including in the Middle East and the Falklands.
Over its production run, more than 5,000 units were built, making it one of the most produced supersonic military aircraft of all time.
Features of the DCS World F-4 Phantom
The DCS World F-4 Phantom module offers a meticulous recreation of the aircraft. From its distinctive appearance to its cockpit systems, every detail is crafted to immerse players in the experience of piloting this Cold War icon.
Key Features
- High-Fidelity Flight Model: The module replicates the Phantom’s handling characteristics, including its high-speed stability and low-speed quirks.
- Detailed Systems:
- Accurate avionics, including radar and weapons control systems.
- Simulated failures for authentic training scenarios.
- Authentic Sound Design: The module captures the roar of the Phantom’s General Electric J79 engines.
- Multi-Crew Functionality: Fly solo or with a human RIO (Radar Intercept Officer) in cooperative multiplayer missions.
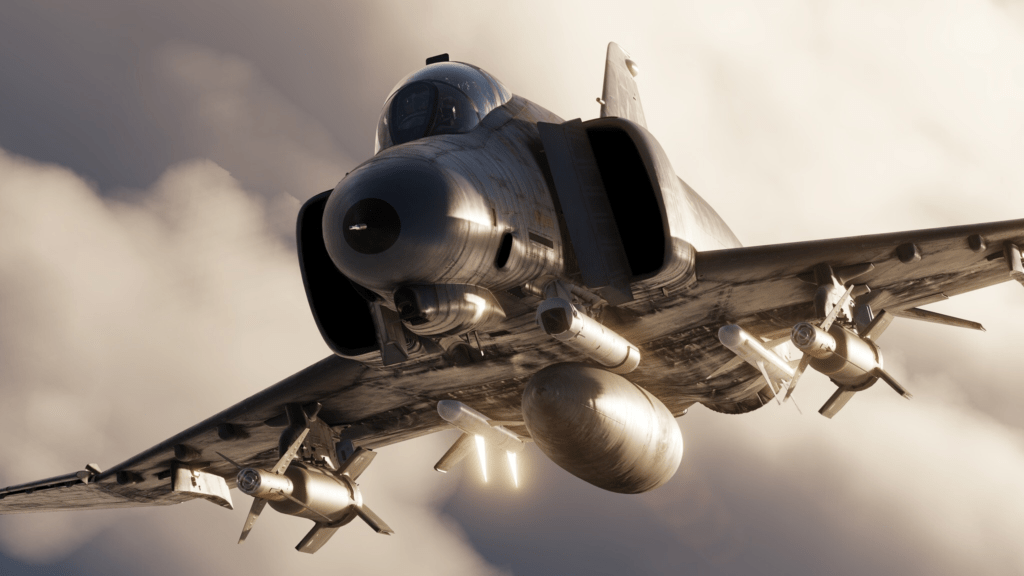

Performance Overview
The F-4 Phantom’s performance in combat was a mix of raw power and inherent design challenges. Powered by two J79 engines, it could achieve speeds over Mach 2.2. However, its large size and weight impacted agility in dogfights.
Critical Performance Metrics
- Corner Speed: Around 420–450 knots, where the aircraft achieves its maximum instantaneous turn rate.
- Sustained Corner Speed: Approximately 390 knots, allowing for continuous turning without losing energy.
- Rate of Turn: At its best, the Phantom could achieve 16–18 degrees per second in ideal conditions. Be prepared to turn in a slight dive to keep your energy. The F-14 had the same requirement where about 7 degrees nose down allowed them to turn best!
These speeds and rates make the F-4 effective in the DCS World air combat environment, provided players leverage its speed and energy tactics instead of trying to out-turn more agile fighters like the MiG-21.
- Latest CPU’s Available Now – Amazon.com
- Get a NEW GPU Best Performance – AMAZON.com
- Upgrade RAM Here today – AMAZON.com
- Prebuilt PC Options – AMAZON.com
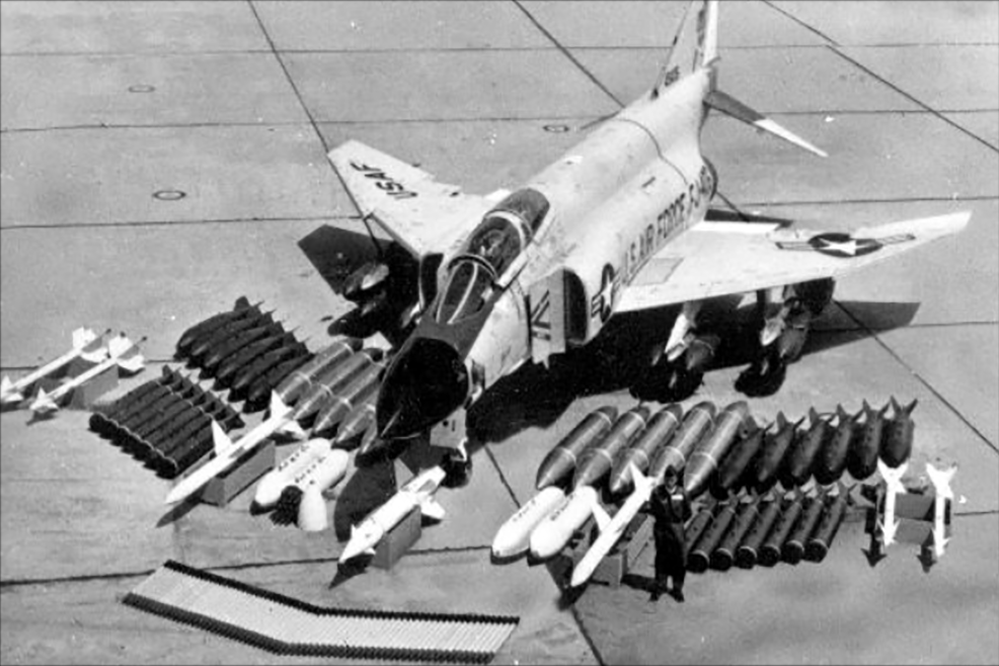

Armament and Loadouts
The F-4 Phantom is a versatile weapons platform, capable of carrying a wide variety of air-to-air and air-to-ground ordnance.
Air-to-Air Weapons
- AIM-7 Sparrow: Semi-active radar-guided missile, effective at medium range.
- AIM-9 Sidewinder: Heat-seeking missile, ideal for short-range engagements.
- M61 Vulcan Cannon: Added in later versions like the F-4E for close-range dogfights.

Air-to-Ground Weapons
- Unguided Bombs: Mk-82, Mk-84, and BLU-series bombs.
- Guided Munitions: AGM-65 Maverick missiles and laser-guided bombs.
- Rocket Pods: Hydra-70 or Zuni rockets for close air support.
Common Loadouts
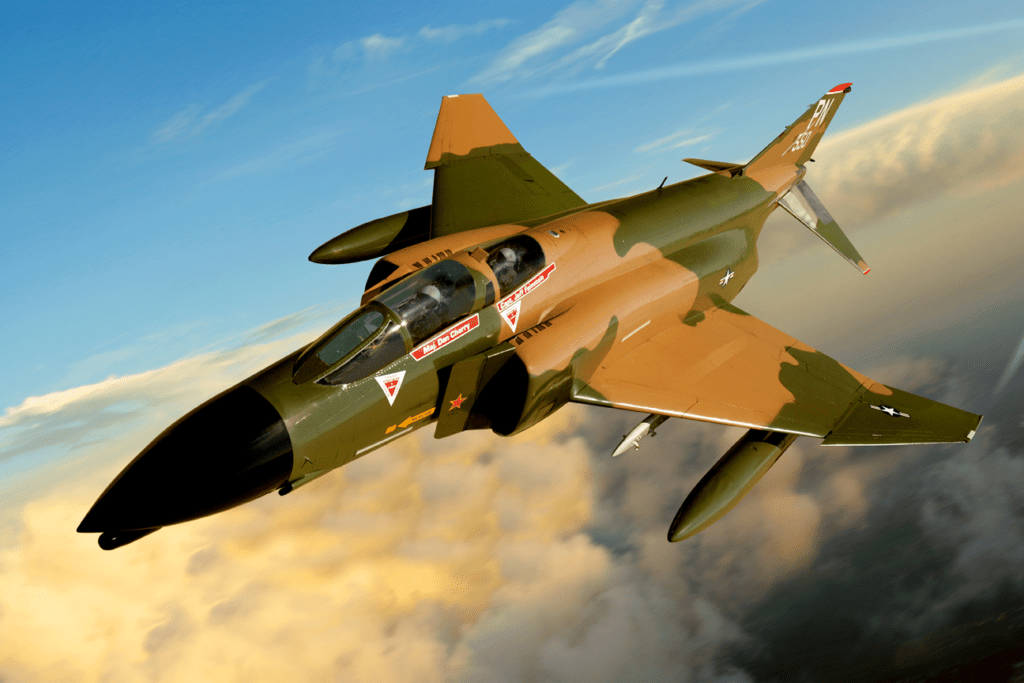
- Air Superiority: 4 AIM-7s, 4 AIM-9s, and external fuel tanks.
- Ground Attack: A mix of unguided bombs and rockets, with two AIM-9s for self-defense.
- Multi-Role: 2 AIM-7s, 2 AIM-9s, and a combination of bombs and rockets.
Comparing the DCS Module to the Real F-4 Phantom
Flight Dynamics
The DCS World F-4 Phantom captures the real aircraft’s balance of speed and weight. It feels heavy in low-speed maneuvers, just as pilots described. The module’s flight model highlights the need for energy management, making it rewarding for skilled players.
Systems and Avionics
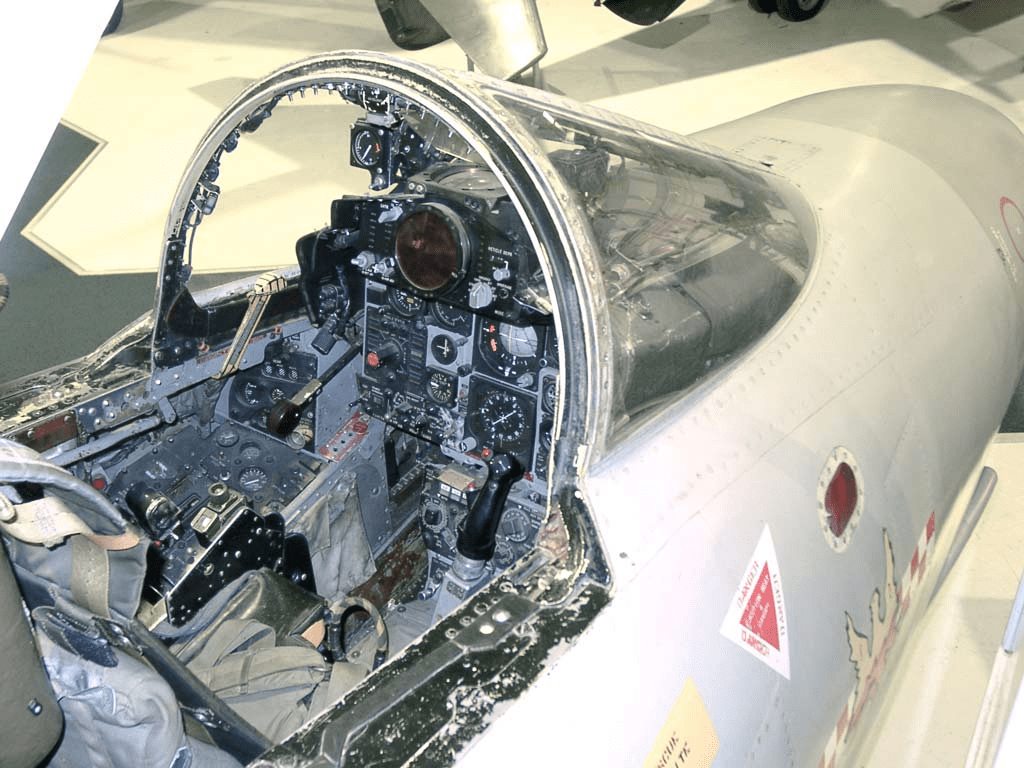
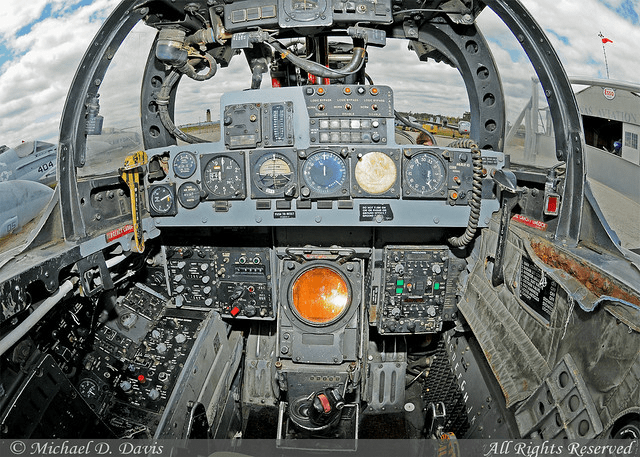
The module closely mirrors the real-world aircraft’s avionics, with detailed radar and weapons systems. While modern fighters use more advanced avionics, the F-4’s systems provide a satisfying challenge for DCS players.
Realism in Combat
DCS World recreates the Phantom’s limitations, such as its lack of a helmet-mounted sight and reliance on semi-active missiles. These constraints require players to adopt real-world tactics, emphasizing teamwork and strategy.
Operational History and Combat Performance
The F-4 Phantom has an illustrious combat history, particularly during the Vietnam War. It performed air-to-air missions, close air support, and strategic bombing.
MiG Kill Statistics

- Confirmed Kills: The F-4 shot down 107 MiGs during the Vietnam War.
- Most kills were achieved with AIM-7 Sparrow missiles.
- AIM-9 Sidewinders accounted for a significant number as well.
- Losses:
- 33 F-4s were lost in air-to-air combat.
- Many losses stemmed from the Phantom’s reliance on missile technology, which was less reliable at the time.
SAM and AAA Losses
- Over 400 F-4s were lost to surface-to-air missiles (SAMs) and anti-aircraft artillery (AAA) in Vietnam. These losses highlighted the need for improved electronic warfare and countermeasure systems.
Common Missions
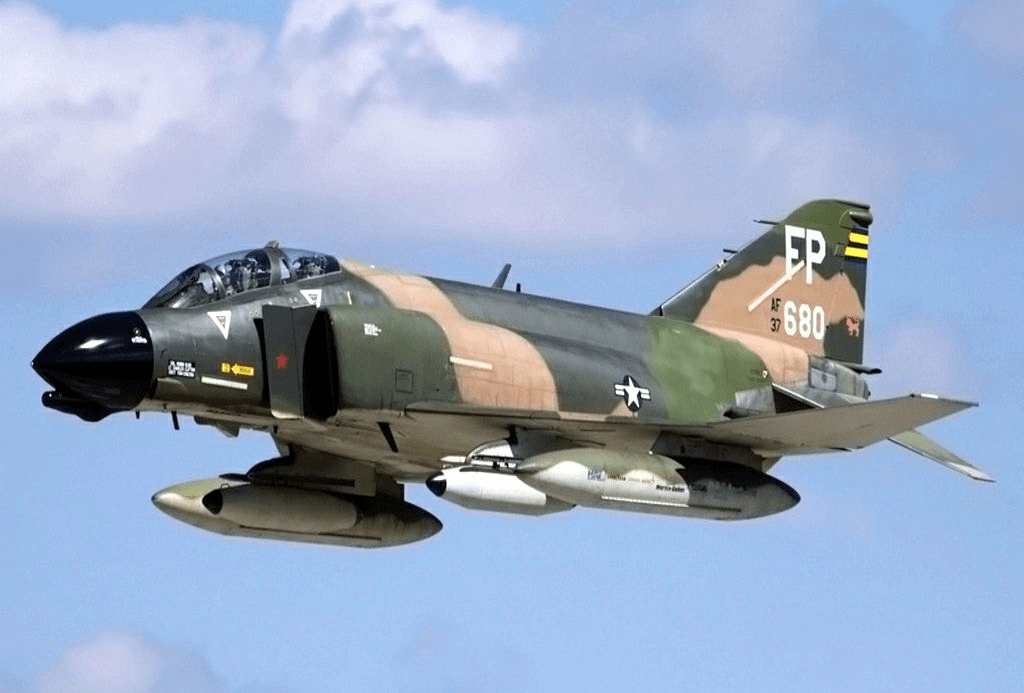

- Air Superiority: Engaging MiGs over North Vietnam.
- Ground Attack: Striking supply lines and enemy positions.
- Wild Weasel: Suppressing enemy air defenses with anti-radiation missiles.
Design Evolution of the F-4 Phantom
The Phantom underwent several significant design changes during its career:
- F-4C/D: Early Air Force versions with basic radar and limited ground-attack capabilities.
- F-4E: Introduced an internal M61 Vulcan cannon to address the lack of a close-range weapon.
- F-4G Wild Weasel: Specialized in electronic warfare and suppression of enemy air defenses.
- F-4J/S: Navy variants with improved radar and avionics.
These changes extended the Phantom’s operational life and enhanced its effectiveness in diverse roles.
Operators of the F-4 Phantom

The F-4 served in the air forces of 11 nations, including:
- United States
- United Kingdom
- Germany
- Japan
- Israel
- Iran
- Greece
- Turkey
- Australia
Each country employed the Phantom in unique roles, from air superiority to ground attack.
Australia and the F-4 Phantom

Australia briefly operated the F-4 Phantom II during the early 1970s. The Royal Australian Air Force (RAAF) leased 24 F-4E Phantom IIs from the United States to temporarily fill the gap between the retirement of the Canberra bomber fleet and the arrival of the General Dynamics F-111C.
Details of the RAAF’s F-4 Phantom Use
- Lease Period: 1970–1973
- Role: The RAAF used the F-4E for air defense and strike roles.
- Operational Squadron: No. 82 Wing at RAAF Base Amberley.
- End of Service: Once the F-111C became operational, the leased Phantoms were returned to the United States.
Despite its short tenure with the RAAF, the F-4 Phantom was well-regarded by Australian pilots, who appreciated its versatility and performance. Its presence in the RAAF marked a key transitional period in Australian military aviation.
Legacy and Popularity in DCS World
The F-4 Phantom remains a beloved aircraft among aviation enthusiasts and DCS World players. Its combination of power, history, and challenge make it a rewarding module for those seeking a balance between technical mastery and thrilling combat.
How It Stacks Up in DCS
- Strengths: Excellent speed, robust weapons loadouts, and versatility.
- Weaknesses: Limited agility and reliance on outdated missile technology.
Despite these challenges, the F-4 Phantom is a testament to the skill and tactics of its pilots, both in real life and in DCS World.
The F-4 Phantom’s enduring legacy and its faithful recreation in DCS World ensure its place as a fan favorite. Whether you’re exploring its historical missions or engaging in multiplayer dogfights, the Phantom offers an unmatched flight simulation experience.
F-4 Phantom II Flight Manual – NATOPS

Dive in as deep as you dare into the F-4 Phantom II Flight manual and be the pilot you always dreamed of NOW! Avialogs – F-4 Phantom II Manuals. External Link till Mine is uploaded soon
- Joystick / HOTAS – AMAZON.com
- Rudder Pedals – AMAZON.com
- Throttle Quadrant – AMAZON.com
- Gaming Chair – AMAZON.com
- VR Headset – AMAZON.com
Author

Brendon McAliece (Aka Gunnie) is a military veteran with 23 years working on Jet Fighters, their weapons systems and ejection seat/module systems as well as munitions and R&D. Involved with flight simulation since the 1980s, he has flown all the major flight simulators over the years.
He is an Australian expat who has lived in Malaysia, UK, Saudi Arabia and more recently Thailand. He is a multi-lingual blogger who loves to share his life experiences here on LetsFlyVFR.com and DreamingGuitar.com, with his lifestyle and Travel experiences Blog plus his Dreaming Coffee website.
Learn More @
DreamingGuitar.com – DreamingCoffee.com – LetsFlyVFR.com
( HOME – BLOG – SHOP – ABOUT )
As an Amazon affiliate I may benefit from qualifying sales.









